Laboratory
* represents those who will not accept new students.Complexity Platform

E-mail: kori@k.u-tokyo.ac.jp
http://www.hk.k.u-tokyo.ac.jp/index-jp.html
To understand natural, biological, and artificial systems, we perform mathematical modeling and analysis. Moreover, closely collaborating with experimentalists of various fields, we try to solve problems related to our lives.
Modeling and Theory Construction
By constructing simple models that describe complex dynamical phenomena, we try to understand, predict, and control such phenomena. Moreover, through the generalizing and abstraction of problems, we try to construct general theories. Examples of our subjects include biological rhythms, locomotion, hydrodynamic phenomena, power grids, transportation networks, traffic networks, pattern formation in biological and chemical systems, social systems, neural networks.
Collaboration with experimentalists
To solve problems closely related to our lives, we collaborate with researchers of various disciplines such as engineering and biology. Our roles are to provide theoretical ideas, to analyze and interpret experimental data, and to propose new experiments.
Keywords
nonlinear phenomena, oscillations, synchronization, fluctuation, complex networks, control, optimization, biological rhythms, circadian rhythms, locomotion, biological physics

E-mail: r-koba@k.u-tokyo.ac.jp
http://www.hk.k.u-tokyo.ac.jp/index-jp.html
To understand the world, e.g. biological and social systems, we are developing a method for modeling and forecasting time series, which were observed from complex systems. We are also applying the method to large dataset from the brain, the internet, and other social systems by collaborating with experts in the respective field. We are currently working in the following projects.
Event time series analysis
We focus on event time series, which means the timestamps of an event, appearing in various systems including tweets on Twitter, log data of product purchases, earthquake, and the action potentials in the brain. We are developing a method for discovering hidden rules underlying an event time series.
Modeling biological and social systems
We are developing a mathematical model that describes the observed data and analyzing the model to understand the way the brain processes information and the information diffusion on the internet. This research has implications for brain-inspired artificial intelligence and a current internet problem of the spread of fake news, misinformation, and flaming.

E-mail: izumida@k.u-tokyo.ac.jp
http://www.hk.k.u-tokyo.ac.jp/index-jp.html
Many systems in our world, natural and artificial systems, are dynamical and are in nonequilibrium states accompanied by energy and mass flow. Their dynamics are typically governed by nonlinear equations. In our laboratory, through mathematical modeling and construction of phenomenological theory of specific systems, we explore fundamental laws that govern the nonlinear and nonequilibrium systems. We also aim at creating new technologies based on these laws. We have been mainly working on the following subjects:
(1) Efficiency bound of heat engines working at maximum power
While maximum efficiency of heat engines is given by Carnot efficiency, it is practically useless because power vanishes at the quasistatic limit. For this problem, we have proposed a finite-time Carnot cycle model and are approaching a fundamental aspect of nonequilibrium thermodynamics and statistical mechanics by investigating efficiency bound of heat engines working at maximum power.
(2) Physics of autonomous heat engines
Low-temperature-differential Stirling engines operate autonomously under quite a small temperature difference between body temperature and room temperature. We have elucidated a rotational mechanism of the engine by developing a nonlinear dynamics model and have been constructing a nonequilibrium thermodynamics theory of the engine. We are also interested in proposing a new type of energy devices.
(3) Energetics of synchronization in coupled oscillators
It is known that flagella of living organisms that play vital role in biological functions can be regarded as self-sustained oscillators and that they synchronize to work via hydrodynamic coupling. We have constructed energetics of synchronization in coupled oscillators and are approaching complex life phenomena by highlighting role of synchronization in biological functions.
(4) Shortcuts to adiabaticity (STA)
STA is a recently proposed method for achieving acceleration of adiabatic quantum dynamics accompanied by sufficiently slow variation of external parameters, which has been receiving attention for its potential applicability. STA has also been applied to adiabatic classical dynamics, and we are investigating an underlying mathematical mechanism of the acceleration.

Tel. 03-5841-4106
E-mail: sugi@k.u-tokyo.ac.jp
http://www.ms.k.u-tokyo.ac.jp/index.html
Developing a Computer That Learns Like Humans
Together with the rapid progress and spread of the Internet and sensor technology,
vast amounts of data are collected in various fields of engineering, industries, and natural sciences such as speeches, images, texts, movies, social media,
E-commerce, power networks, medicine, and biology.
To create new value from such big data, machine learning plays a central role.
Machine learning is aimed at developing a computer that learns like humans.
Our group studies various aspects of machine learning and statistical data analysis
such as fundamental theory, practical algorithms, and application to real-world data analysis.

Tel. 04-7136-3956
E-mail: yokoya@k.u-tokyo.ac.jp
http://www.ms.k.u-tokyo.ac.jp/index.html
Understanding What's Happening on Earth from Multimodal Spatio-Temporal Data
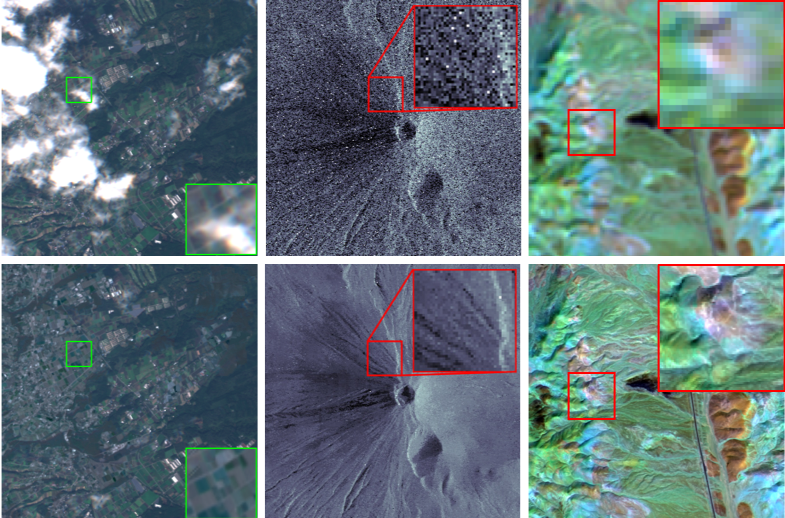
We are studying geoinformatics to understand the current state of the Earth from multimodal spatio-temporal data such as satellite images, mobile data, and disaster data. In particular, we are working on intelligent data analysis based on image processing and machine learning to understand what is happening on the Earth in a timely manner from a large and diverse set of images obtained from visible, near-infrared, thermal infrared, and microwave based remote sensing.
(1) Beyond human vision
Data obtained by spectroscopic imaging and synthetic aperture radar allow us to see the world invisible to humans, but there are imperfections due to sensor characteristics and atmospheric conditions. Based on mathematical optimization, machine learning, and signal processing, we aim to further advance our sensing technology beyond human vision by recovering the original signal from incomplete multidimensional observation data.
(2) Understanding Earth today
In an emergency such as a disaster, it is important to get a full picture as quickly as possible. We are developing data fusion technology that extracts change information from spatio-temporal data obtained from a variety of sensors on different platforms, from satellites to the ground, and technology that can rapidly estimate unexpected complex changes on the ground surface by combining machine learning and numerical simulation.
(3) Towards a sustainable society
We are conducting research to support solutions to international social issues, such as disaster monitoring and forest monitoring. Our goal is to contribute to the realization of a sustainable society globally by working closely with the world-leading space agencies and disaster prevention organizations to explore technologies that are truly useful in solving real-world problems.

E-mail: ishi@k.u-tokyo.ac.jp
http://www.ms.k.u-tokyo.ac.jp/index.html
Machine learning is the process of a computer learning to extract patterns or knowledge from data. For example, machine learning is used in voice recognition, image recognition, and anomaly detection. In recent years, we are starting to see machine learning being used in various areas and industries, and the need to handle new types of data and tasks is increasing, leading to a higher demand for better machine learning technology.
In our lab, we are working on fundamental research on machine learning algorithms. There are many challenges in machine learning that we work on: How can we generalize better to unseen data? How can we learn from weak supervision? How can we make the algorithm robust? How can we make a general framework that can be applied to different tasks or problems? Through our research, we are aiming to develop practical and reliable machine learning technology.

— we build what comes after
As computational power has grown dramatically and real-time coupling between simulation and physical control has become feasible, the very boundary between computation and nature has begun to shift. We envision and work toward "Digital Nature," an environment in which computation and the natural world overlap indistinguishably, seeking both to elucidate its principles and to implement them.
With high-speed loops that cycle between in-silico simulation and in-situ physical experimentation as our central methodology, we conduct research across computational optics, acoustics, human-computer interaction, and digital fabrication.
(1) In-Silico/In-Situ Fusion and Multimodal Information Processing: We build knowledge representations by combining differentiable programming with large-scale language and vision models, and design systems that project simulation results into physical space as light, sound, and force through high-speed spatial light modulators and ultrasonic phased arrays. We develop frameworks for integrated multimodal input/output spanning vision, audition, and haptics.
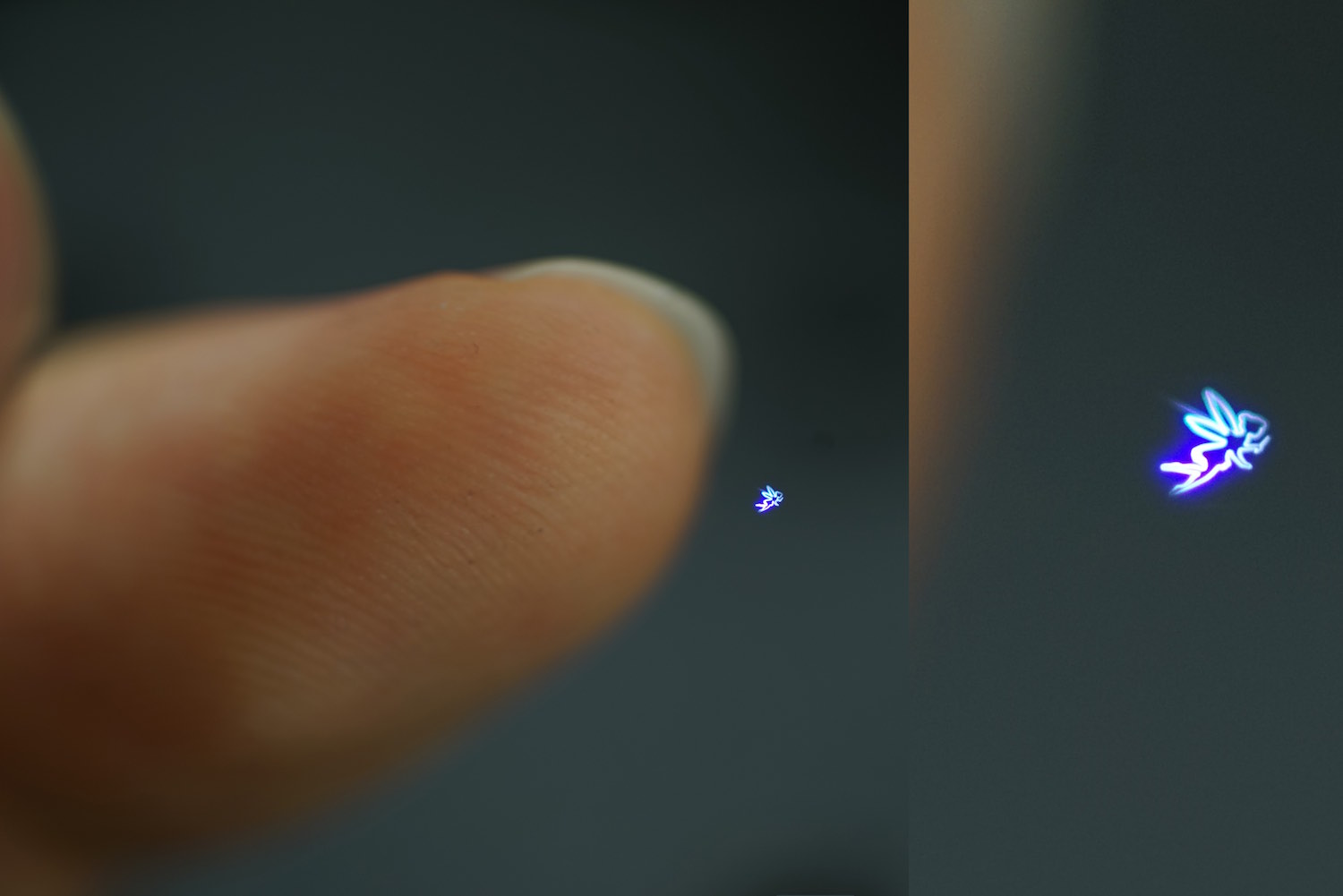
(2) Computational Optics and Wave-Field Control: We study display and manipulation devices based on computational control of light and sound waves, including aerial plasma emission via femtosecond lasers (Fairy Lights in Femtoseconds), 3D image generation through computer holography, and mid-air haptic display and acoustic levitation using ultrasonic phased arrays.
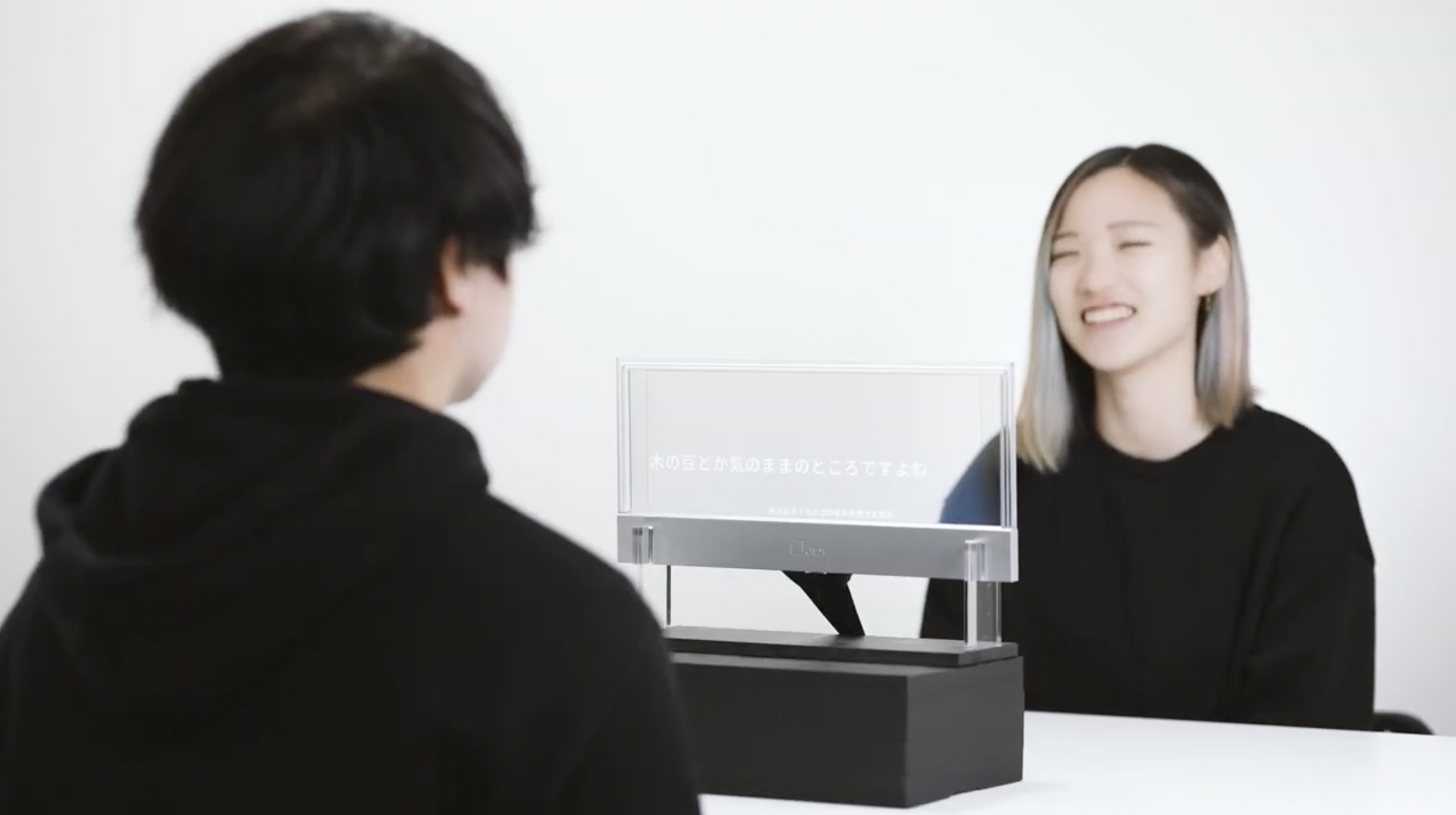
(3) Accessibility and Inclusive Design: Aiming to realize environments in which people with diverse embodiments can access information equally, we develop and deploy assistive technologies such as See-through captions, a speech-to-visual device for deaf and hard-of-hearing users. We pursue assistive foundations that transcend specific types of disability through computational cross-modal "translation."
(4) Media Art and Social Implementation: We examine the ideas of Digital Nature through both artistic creation and social deployment. Through projects including the null² Pavilion at Expo 2025 Osaka, we explore the interface between technology and society by bringing spaces where computation and matter intersect into the physical world.

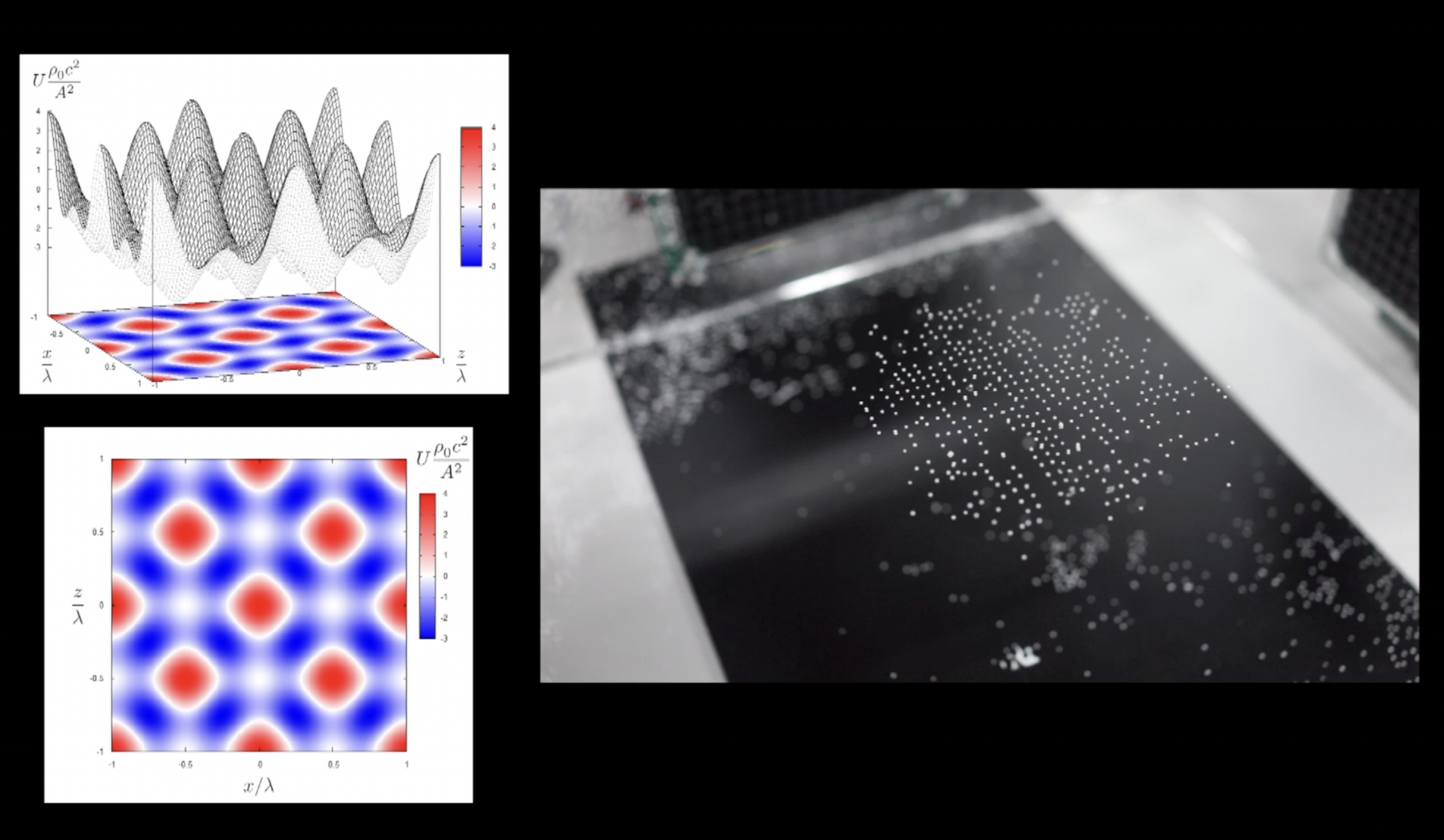


2) Acoustic levitation via ultrasonic phased array — Small objects held and manipulated in mid-air by ultrasonic standing waves. Demonstration of wave-field control technology
3) See-through subtitle display — Real-time subtitles displayed on a transparent screen to support face-to-face communication. Social deployment of accessibility research
4) null² Pavilion — Exterior of the thematic pavilion at Expo 2025 Osaka
Brain-Bio Module

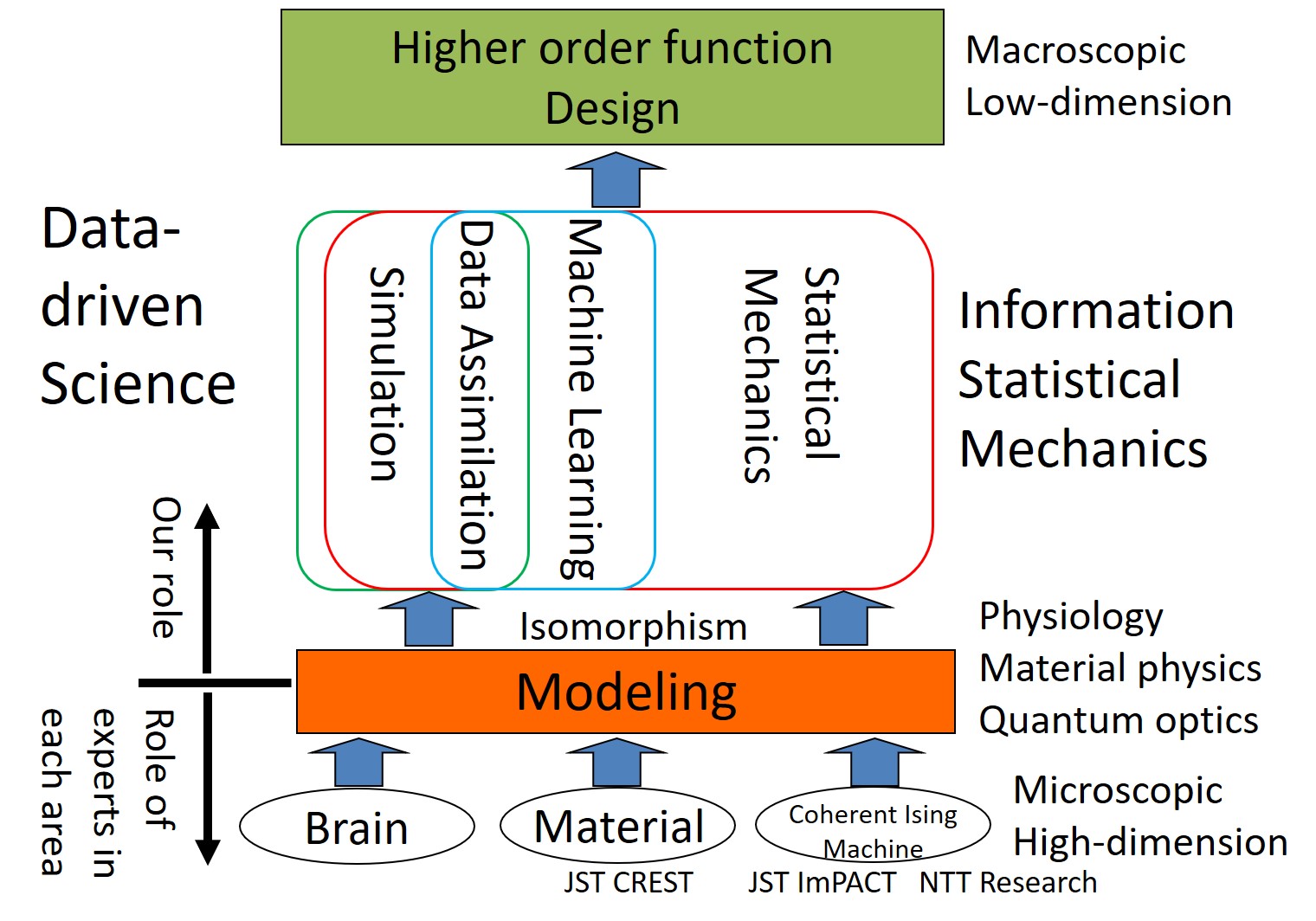
We focus our research on neuronal systems and functional materials such as batteries, optical computers, and so on. Despite appearing unrelated, they have a common mathematical structure, namely, isomorphism, as a system. In collaboration with experimental and theoretical researchers, we model and apply machine learning methods and statistical mechanics based on the isomorphisms of these subjects and conceptualize these higher-order functions. Through such a cross-disciplinary approach, different subjects can be understood in a universal manner.
Analyses of the nervous system and functional materials using imaging techniques
In recent years, new imaging techniques have been developed in several research fields, including neuroscience and materials science. Mathematical models for imaging processes are often isomorphic. By utilizing the isomorphism, we propose effective methods for the analysis of imaging problems for which machine learning has not yet been applied.
Cross-disciplinary application of non-equilibrium information statistical mechanics
It is possible to describe neuronal systems, magnetic thin films, and optical oscillators as nonlinear oscillators by isomorphic canonical models. The isomorphism has helped us clarify the macroscopic properties of subjects in which non-equilibrium information statistical mechanics has not been applied. As an example, we proposed a method for implementing compressed sensing, which is a fundamental method in the area of data-driven science, with the Coherent Ising Machine, and clarified theoretically its performance limits.
A message for everyone
Several decades ago, neuroscience and artificial intelligence were considered to belong to the same field. However, as the number of researchers has increased and research has become more sophisticated, it has been classified into a wide variety of research fields. Many researchers are increasingly realizing that the subdivision of research fields has negative consequences. The purpose of our work is to create reverse flow against the subdivision. Don't you want to become the ultimate generalist?

Tel. 04-7136-4085
E-mail: okada@k.u-tokyo.ac.jp
http://mns.k.u-tokyo.ac.jp
今,脳と物質のデータ駆動科学の創成を目指す』
Theoretical neuroscience, Statistical physics


Tel. 04-7136-3900
E-mail: hiroyuki_shinoda@k.u-tokyo.ac.jp
http://www.hapis.k.u-tokyo.ac.jp/public/hiroyuki_shinoda/
情報環境を革新する』
Haptics:
We investigate technical and scientific issues related to haptics.
Our goal is to develop a human activity support system while clarifying the physical mechanisms of the human tactile organ
and relationships between haptic stimulation to humans and human responses in physical actions and mental statuses.
Two-dimensional communication:
This relates to research on signal and power transmission with electromagnetic waves traveling along a thin sheet.
The technology enables a wireless and battery-free information environment that provides safe wireless power transmission to items touching the sheet
and high-speed signal transmission with low interference from ordinary wireless signals. This technology also contributes to wearable computing and sensor embedding in various elastic materials.




Tel. 04-7136-3912
E-mail: yasutoshi_makino@k.u-tokyo.ac.jp
http://www.hapis.k.u-tokyo.ac.jp/?page_id=1002
触ること・触られることの本質を探る』



Tel. 04-7136-3919
E-mail: nose@k.u-tokyo.ac.jp
http://bio.phys.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp/
神経回路の機能と構造にその答えを探る』
We are interested in the mechanisms of how the neural circuits develop and function to generate specific behavior, by using the nervous system of the fruit fly Drosophila as a model. In this organism, the relative simplicity and highly sophisticated genetic techniques allow one to identify and manipulate specific neurons. We focus on the larval peristalsis (waves of muscular contraction that propagate along the body) and try to understand how the motor outputs are generated by the neural circuits. For this, we use a variety of genetic and biophysical techniques. For example, we use calcium imaging to record the activity of specific population of neurons. By using a recently developed technique, called optogenetics, we manipulate the activity of specific neurons with light at high resolution. By recording and manipulating the spatio-temporal pattern of neural activity, we aim to understand the operational principle of the neural circuits.



E-mail: hayashi@issp.u-tokyo.ac.jp
https://www.issp.u-tokyo.ac.jp/maincontents/organization/labs/hayashi_group_en.html
Precise physical measurements are important for cells to understand molecular mechanisms occurred in cells as well as for solid state materials. However, in vivo measurements are difficult because intracellular environments are complex non-equilibrium states, in which theories of statistical physics are often violated.
In our lab, we develop techniques to precisely measure physical quantities such as force, velocity and energy for proteins and organelle inside cells, based on fluorescence microscopy. We think development of analytical methods (software) using statistical physics, information science and mathematics as well as development of microscopes (hardware). We aim to understand cellular phenomena quantitatively by constructing theoretical models using the measured physical quantities. We hope such theories can contribute to the understanding of neurological disorders particularly.
Biophysics is a new field and it will grow in future. People who are interested in biology from the viewpoint of physics are welcome. Because we belong to Biophysical Society, people who speak English are also welcome.
Research topic 1:Fluorescence observation of axonal transport in iPS cell derived neuron
Materials synthesized in the cell body of a neuron are transported by motor protein (kinesin and dynein)
along the axon (axonal transport). Because this logistics is important for neurons, deficits of axonal
transport is related to neurological disorders [1]. We apply non-equilibrium statistical physics to time
course analysis of axonal transport, we measure physical quantities such as force, velocity, number,
entropy production of motor proteins [2].
Research topic2:Force measurement of motor protein kinesin by using a nano-sized spring
Kinesin is a motor protein in charge of axonal transport. Its force has been measured by using optical
tweezers (Nobel Prize in Physics 2018) [3]. As a substitute of optical tweezers, we aim to measure
its force by using nano-sized spring, made of DNA-origami, developed in the previous study [4]. We try to
develop the force measurement using the spring in order to measure transport force of motor proteins inside
cells.
Research topic3:Extreme value analysis applied to axonal transport by motor proteins
We obtain information on force of motor proteins engaging in axonal transport, by applying extreme values
analysis to transport velocity data, noting that in vivo force measurements are difficult in general.
We performed in vivo fluorescence observation of axons inside living C. elegans worms, and found the
difference of force generation mechanism between kinesin and dynein [5].
Research topic4:Theoretical modeling of synapse formation related to axonal transport
We aim to construct theoretical models to explain synapse formation. It has been known that KIF1A
mutants cause abnormal synapse formation, where KIF1A is one kind of kinesin family transporting synaptic
materials [6]. We try to relate “physical properties of KIF1A mutants (force, velocity, number)” and
“those of synapses (size, interval, position), to contribute to understanding of KIF1A associated
neurological disorder [1].
Reference
[1] KIF1A.org
[2] Hayashi, et al., Mol Biol Cell 2018;Phys Chem Chem Phys 2018; Sci Rep 2019
[3] Svoboda, et al., Nature 1993
[4] Iwaki, et al., Nat Commun 2016
[5] Naoi, et al., bioRxiv 2021
[6] Niwa, et al., Cell Rep 2016

E-mail: shigeyoshi.fujisawa@riken.jp
https://cbs.riken.jp/en/faculty/s.fujisawa/
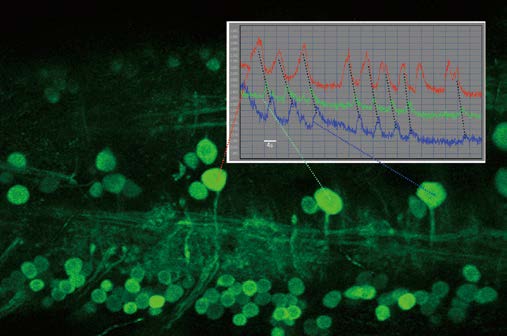
Our main research goal is to elucidate the neuronal and network mechanisms underlying reward-related cognitive functions, particularly the contribution of the dopaminergic circuits of the basal ganglia, the prefrontal cortex and the hippocampus. Studying the physiological mechanisms of cognitive functions requires understandings not only the responses of single neurons to external stimuli but also circuit computations at the level of networks of neurons during cognitive processing. To understand the 'syntax' underlying neuronal communications, methods for monitoring and quantifying cooperative neuronal activities during cognition are required. To this end, we have been performing large-scale high-density recordings of local circuits with multi-channel silicon probes, enabling the observation of simultaneous neuronal firing activities in up to 100 neurons, as well as local field potentials in behaving animals. In addition, we are developing a new technique that combines large-scale recording and targeted simultaneous optogenetic stimulations of specific cells, such as dopaminergic neurons, to clarify the role of the different types of neurons in network processing, in freely behaving mice. Taking advantage of these methods, we try to decipher circuit computations within local and between the inter-regional networks during reward-related cognitions such as decision making and working memory.

Astrobiology Module

E-mail: t_imamura@edu.k.u-tokyo.ac.jp
http://www.astrobio.k.u-tokyo.ac.jp/imamura/english/
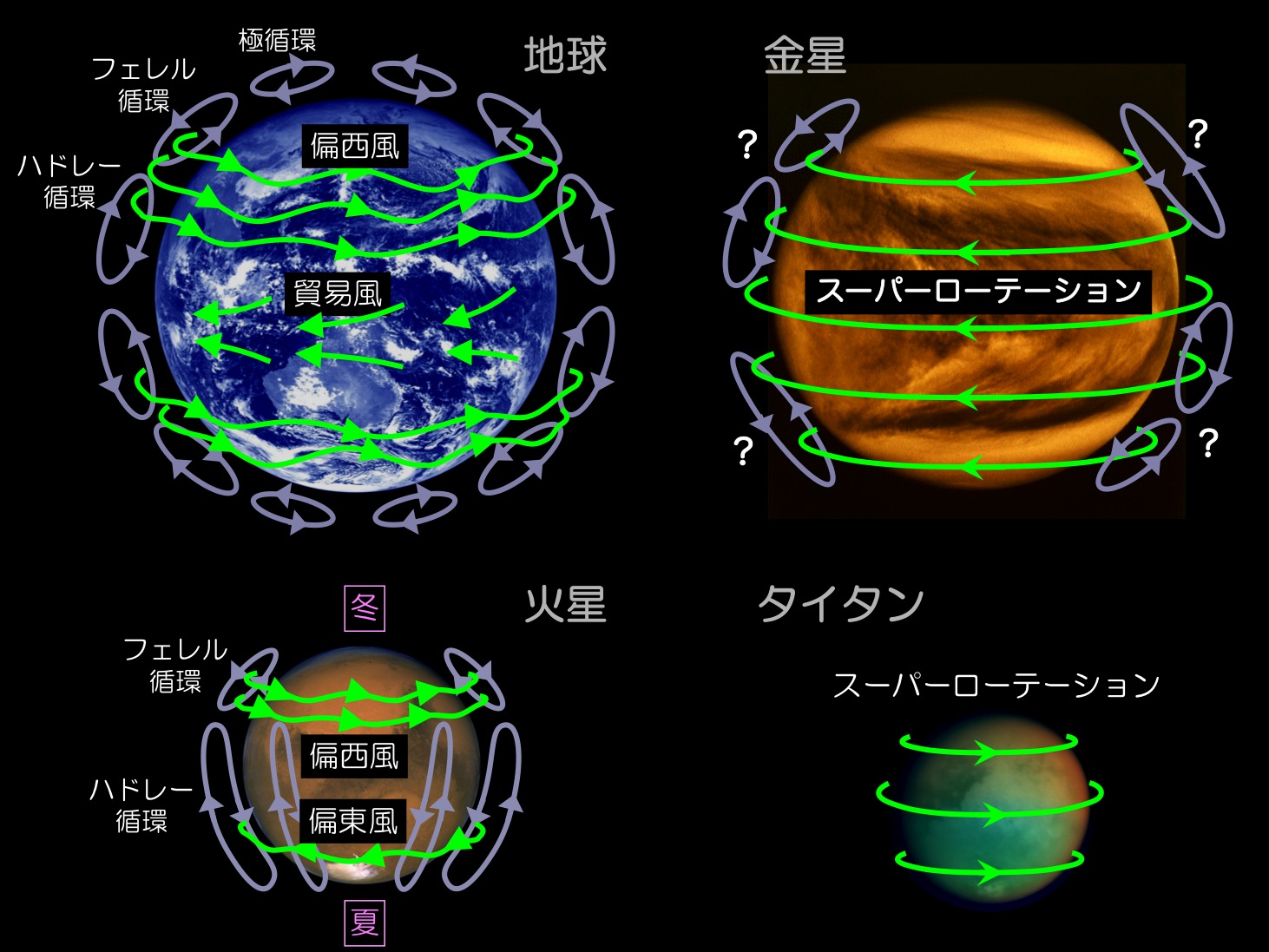
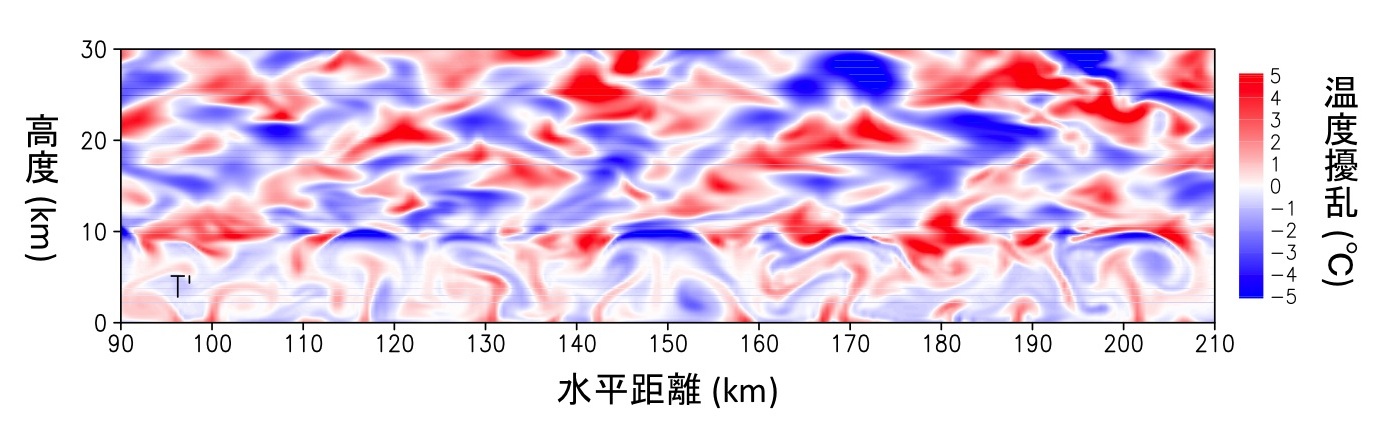
The circulation of energy and substances in a planetary atmosphere controls the development of the planetary environment, thereby governing the possibility of a biosphere. The planetary atmospheres observed so far show surprising diversity, whose origin is still unclear. Our laboratory focuses on planetary atmosphere physics and resultant climate formation. The ultimate goal is general understanding of common physical processes behind the apparent diversity. The following observational and theoretical approaches are ongoing.
(1) Exploration of planetary atmospheres
Exploration of Venus atmosphere by a Japanese Venus explorer AKATSUKI is ongoing.
We use AKATSUKI's data to unveil the mysteries of Venusian meteorology such as the high-speed
westward circulation "super-rotation" and thick sulfuric acid clouds.
Development of a Mars exploration program including the studies of water cycle and dust transport is also ongoing.
In a radio occultation experiment, a spacecraft transmits radio waves toward a tracking station on the earth and sequentially goes behind the planet's atmosphere; during such occultation events the planetary atmosphere cause frequency and amplitude fluctuation, from which information on the atmosphere is obtained. We apply this technique to planets and the solar corona. (3) Numerical modeling
Common physical processes behind the apparent diversity of atmospheric phenomena on the planets are investigated with numerical modeling and theories.

Tel. 04-7136-3948
E-mail: shohei.aoki@edu.k.u-tokyo.ac.jp
https://www.astrobio.k.u-tokyo.ac.jp/imamura/
How does a habitable planetary climate make and sustain? - The ultimate goal of our research is to answer such a question.
Our planet, the Earth, has been investigated from this point of view for many decades. On the other hand, in this century, Earth-like planets have been discovered outside of our solar system. In the next decades, it will be required to study atmosphere of terrestrial planets as a common system. However, it is still challenging to directly observe atmosphere of the Earth-like exo-planets. Thus, it is important to investigate the atmosphere of Mars and Venus that are "Earth-like planets" in our solar system, and to understand their environment and evolution.
It has been proposed hat Mars (and probably Venus) once had a large amount of liquid water on the surface like the current Earth. However, the current Venus has extremely warm climate with thick CO2 atmosphere, and Mars is a cold and dry planet. Where/how has a large amount of water gone? To answer such a question is one of the major science goals of recent Mars/Venus missions.
I have studied the atmosphere of Mars with European Mars missions such as Mars Express and ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter, and ground-based telescope observations such as Subaru, SOFIA, ALMA, and IRTF. To improve our observational knowledge of water evolution on Mars and Venus, I analyze new data from the Mars orbiters with NASA/ESA colleagues and perform new observations with ground-based telescopes.
One of the interesting aspects of the planetary science is that there are a lot opportunities to work with many people as an international team. Please contact us if you would like to join.




Tel. 04-7136-5520
E-mail: yoshikawa@k.u-tokyo.ac.jp
http://www.astrobio.k.u-tokyo.ac.jp/yoshikawa/
観測機を開発し,深宇宙へ送り出す』
地球が,豊かな生命の星でいられるのはなぜだろうか?
私達は,地球のこと,太陽系のこと,宇宙のことをどれだけ理解しているだろうか?
生命が生きてゆくには,湿潤な環境と宇宙放射線から体を守るバリア(惑星磁場)が必要である.
太陽から程よい距離にできたことが,地球における生命発生の理由の一つだが,大気はいつ発生し,湿潤な環境はどのように維持されてきたのだろうか?
火星や金星は生命にとって,どれほど苛酷な環境なのだろうか? 地球の大気環境は変化しないのだろうか? 火星のようになったりしないだろうか?
これらの謎と大気の多様性を解明するために,我々の研究室では,目に見えない特殊な光を用いた観測機を開発している.
この観測機を太陽系内惑星探査機や宇宙ステーション,地球を周回する衛星に搭載し,太陽系惑星を走査し,惑星大気の成分や運動を分析する.
2013年9月にイプシロンロケットで打ち上げられた惑星分光観測衛星「ひさき](SPRINT-A)は,極端紫外光の目を持つ “宇宙望遠鏡” である.
極端紫外光は,紫外線の中でも波長の短い光で,この光で見た地球は,ふだん私たちが見ている青くて丸い地球とはずいぶん違って見える.
例えば,北極と南極を付け根にして,地球半径の5~6倍の空間に広がる蝶のような姿(双極子磁場)に満たされたプラズマ(電離した気体)が写る.
極端紫外光で他の惑星を観測すれば,地球との差異だけではなく,惑星大気の生成過程も解明できるだろう.これらの知見を元に観測対象を拡大し,「太陽系外の生命探査」を行うことが究極のテーマだ.




E-mail: kazuo.yoshioka@edu.k.u-tokyo.ac.jp
https://www.astrobio.k.u-tokyo.ac.jp/yoshikawa/member/yoshioka/

Tel. 050-3362-4196
E-mail: tanaka@planeta.sci.isas.jaxa.jp
http://planetb.sci.isas.jaxa.jp/luna/index.html
太陽系探査の最先端の現場を肌で感じよう』
世界に比類がなくわが国独自の月惑星探査を遂行するための探査機器の開発およびプロジェクトの遂行を行っている. これまでJAXA(宇宙科学研究所)において「かぐや」,「はやぶさ」などの月惑星探査を成功させてきたが, それらに続くものとして月着陸探査ミッション(SELENE-2)やC型小天体サンプルリターンミッション(はやぶさ2)などが進められている. これらのミッションの科学的側面から探査戦略の追及,それを実現するたの搭載器機の性能をつきつめて実現化し, 世界トップクラスと賞されるだけでなく将来にわたって活用し続けられるデータの取得を目指す.
これからの月惑星探査の主流は内部構造探査である.これを遂行するための搭載インフラや機器(地震計や熱流量計)の開発が重要である. 我々は長年にわたり地震計などを搭載可能なペネトレータとよばれる高速貫入型の観測装置の開発に携わり,技術的に高いレベルにまで完成させた. 我々が開発したこの装置を月惑星に送り込んで内部構造に関するデータを取得し,月惑星の起源と進化に重要な制約条件を得ることが私の究極的な目標である.
科学的な専門分野は月惑星内部構造論であり,アポロミッションで得られた地震(月震),熱流量などの地球物理学的観測データの解析を行っている. 40年前に取得されたデータでありながら,まだ我々が見出していない真理がまだ多く埋もれているのは驚きでもありまた感動的でもある.



Tel. 03-5841-2830
E-mail: hm@um.u-tokyo.ac.jp
http://www.um.u-tokyo.ac.jp/hp/miyamoto/
惑星や衛星などの表面を調べよう』
惑星探査技術の進歩により,太陽系の天体に探査機を送り込んで調査することが可能となった. 火星探査車は砂だらけの火星表面を走り回り,小惑星探査機は,弾丸を使って岩石を破砕し岩石サンプルを収集した. 人類は,こうした太陽系の直接探査を通じて地球外の天体に関する情報を猛烈な勢いで獲得している. 太陽系科学は,革命的な発展を遂げていると言って良い.
私たちの研究室では,太陽系探査に直接関連した,以下の2つの方向性の研究を推進している. 1つ目は,探査データの解析である. 特に天体の表層環境に関する研究に重点を置いており,主に固体天体表層地形の解析を通じて,地球表層環境の持つ普遍性と特異性を明らかにするという, 比較惑星学(特に惑星地質学)分野の研究を行っている. 「人類が地球に誕生した事に必然性が存在するか」というアストロバイオロジーの大問題に,惑星探査データの解析から迫ろうとしているとも言える.
2つ目は,惑星探査計画への参画である.これまで火星探査機「のぞみ」や小惑星探査機「はやぶさ」,月探査機「SELENE」などの固体惑星探査プロジェクトにおいて微力を尽くしてきたが, 現在は次期小惑星探査計画や月探査計画に参加すると共に,杉田研究室などと共同で,火星着陸機を中心とした複合探査計画を推進している.
こうした研究を進めるには,前者は理学,後者は工学のセンスが重要となるが,実際には双方の知識が必要となる. これらを融合したアプローチを創出し,複雑系という枠組みで新たな太陽系科学を創成することが,私たちの大きな目標である.




Tel. 04-7136-5520
E-mail: sugita@k.u-tokyo.ac.jp
http://www-space.eps.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp/~sugita-lab/
C型小惑星に残る惑星大移動の痕跡』
私は,惑星の起源と進化を理解するため,室内実験と惑星探査の両面から研究を行っている. 室内実験では,惑星初期進化で支配的な役割を果たした小天体衝突の機構解明に力を注いでいる. 地球の基本形が作られた地球集積期やその直後の時代の表層環境の解明が目的である. 特に,大気圏や水圏の質量と組成を決定する衝突蒸発現象機構の解明のため,高速度衝突実験と高速分光計測を用いた研究を行っている. こちらは,自分だけの自由な発想で行えるタイプの研究である.
惑星探査は,他の惑星や衛星を調査して,地球との違いを明らかにすることが目的である. 2014年の打ち上げを目指す「はやぶさ2」計画に参画し,可視分光カメラ開発のサイエンス担当者を務めている. 米国がOSIRISRex計画を打ち出したので競争が大変だが,日本の計画を米国がまねた珍しいケースであり,競争の甲斐もある. どちらも水や有機物を豊富に含んだC型小惑星から試料を持ち帰る計画である. 可視分光カメラは小惑星上の物質分布や地形を調べ,どこから試料を採るか決めるための重要な情報を得る. こちらの研究は,大型プロジェクトの動向に左右されるリスクもあるが,宇宙を実感できるメリットがある.
さらに,将来の月や火星の着陸探査計画を見据え,レーザーを用いた元素組成計測装置(LIBS)やK-Ar法を用いたその場年代分析装置の開発も進めている.


Extreme Matter Module

Tel. 04-7136-3926
E-mail: ejiri@k.u-tokyo.ac.jp
http://fusion.k.u-tokyo.ac.jp/~ejiri/
Plasma consists of charged particles, which generate electric and magnetic fields, and they interact via electromagnetic forces. In high temperature plasmas, however, low collisionality and low diffusivity prevent an equilibrium. From these two features, high temperature plasmas often become a nonlinear and non equilibrium system. One of the approaches for these issues is fluctuation measurements. In our laboratory, we are developing advanced diagnostics and analysis algorithms for fluctuation measurements, as well as conventional plasma physics. Our main target plasma is the TST-2 spherical tokamak plasma in our laboratory. In addition, we study also LHD plasma in Gifu, QUEST plasma in Fukuoka, LATE plasma in Kyoto, MAST plasma in UK as collaboration research.




Tel. 04-7136-3878
E-mail: tsujii@k.u-tokyo.ac.jp
https://fusion.k.u-tokyo.ac.jp/index_e.html
Creating an ideal energy source
Massively parallel computing reveals the physics of fusion plasmas
Fusion energy has the potential to generate base-load electricity in a clean and safe way. Although a tokamak based fusion reactor is now expected to be able to create net energy, there are still many topics which need further research to realize a commercial reactor, such as improvement of plasma confinement and establishment of steady-state operation scheme. In our laboratory, with Professor Ejiri, we study basic plasma physics and develop technologies which may lead to faster realization of fusion. On the TST-2 spherical tokamak at the University of Tokyo, we perform experiments with a tokamak plasma driven by RF waves which can be operated in steady-state. We also collaborate with world-leading fusion research groups at institutes such as NIFS and MIT. Simulation of fusion plasmas often requires simultaneous treatment of a wide range of spatial and temporal scales, and description of the phase-space dynamics, which, in turn, requires large computational resources. Recent development of massively parallel computing technology has allowed us to describe fusion plasmas with many interacting physics, with accuracy sufficient to make quantitative predictions. On TST-2, microwave interferometer and hard X-ray radiation measurement is developed and installed to validate the predictions of the simulations. By comparing the experimental measurements with the numerical simulation performed at the supercomputer on NIFS, we are slowly gaining better understanding of wave propagation and damping prcoesses, and interaction between current drive and magneto-hydrodynamic equilibrium.


Tel. 04-7136-3910
E-mail: takehiko@k.u-tokyo.ac.jp
http://sas.k.u-tokyo.ac.jp/index.html
サステナブルテクノロジーを創造しよう』
物質変換の基礎となる触媒の開発・反応機構の研究・機能性界面の創成・表面科学的研究を行っている. また,これらの応用として,二酸化炭素の転換を様々な方法で行い,低炭素化に貢献するための研究を行っている.
(1)新規固体触媒の開発
化学反応を実現する際には,多くの場合に触媒が不可欠となる.
特に,固体触媒は,生成物からの分離が容易で,再利用にも有利なことから実用的な意味が高い.
不活性分子の有用物質への変換を目指して,ナノ金属酸化物結晶,金属錯体をベースにした固体触媒,メソポーラス金属酸化物の開発を行っている.
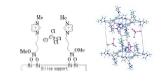
(2)固定化イオン液体の開発
イオン液体は有機物であり,かつイオン対から構成される塩であることから物性のデザインが可能な溶媒として注目を受けている.
我々は,イオン液体分子を固体表面に固定化して(下図参照)固体触媒として有用であることを示している.
イオン液体は二酸化炭素との親和性が高いことからこの性質を利用した反応を開発している.
(3)固体表面上の電子・光励起ダイナミクス・プラズマ誘起化学反応の研究
電子線や光を入射することにより固体表面上の電子状態を励起することで,化学結合の切断や組み替えが起こる.
これらのダイナミクスは光触媒作用とも直接かかわる重要なプロセスである.パルスの電子線,レーザーパルスを入射した後のイオン発生,
発光現象を時間分解測定するための装置開発,およびそれらを用いたダイナミクスの研究を行っている.
また誘電体バリア放電による大気圧近傍のプラズマを利用した化学反応過程の研究を行っている.
(4)計算化学的手法による表面過程・触媒反応の研究
計算化学的手法は現在非常に重要かつ有用なツールとなっている.
我々は,1)モンテカルロ法による固体表面上の吸着種の振る舞いと化学反応の記述,2)遺伝的アルゴリズムを取り入れたテンソルLEED法による複雑な固体表面構造の解析,
3)密度汎関数法による触媒の活性構造と反応過程の解明に取り組んでいる.
化学または物理のバックグラウンドを持つ皆さんに是非一緒に研究に取り組んでいただきたいと思います.



Tel. 04-7136-4044
E-mail: shinohara@k.u-tokyo.ac.jp
https://pp4nf.edu.k.u-tokyo.ac.jp
Ultimate energy to sustain civilization for eternity
In the space far from the Sun, say beyond the orbit of Mars, where the energy supply from the Sun is very limited, our spacecrafts and settlements have to rely on the energy from nuclear reactions. One of the reactions, nuclear fission, is difficult to sustain since it is almost impossible to find its fuel, uranium or other heavy atoms. On the other hand, the fuel of fusion reactions – hydrogen – is widely available in the Universe. (In fact, hydrogen is the source of the power of the Sun.) We should secure such an ultimate energy source, nuclear fusion, to sustain "human civilization" in the long run.
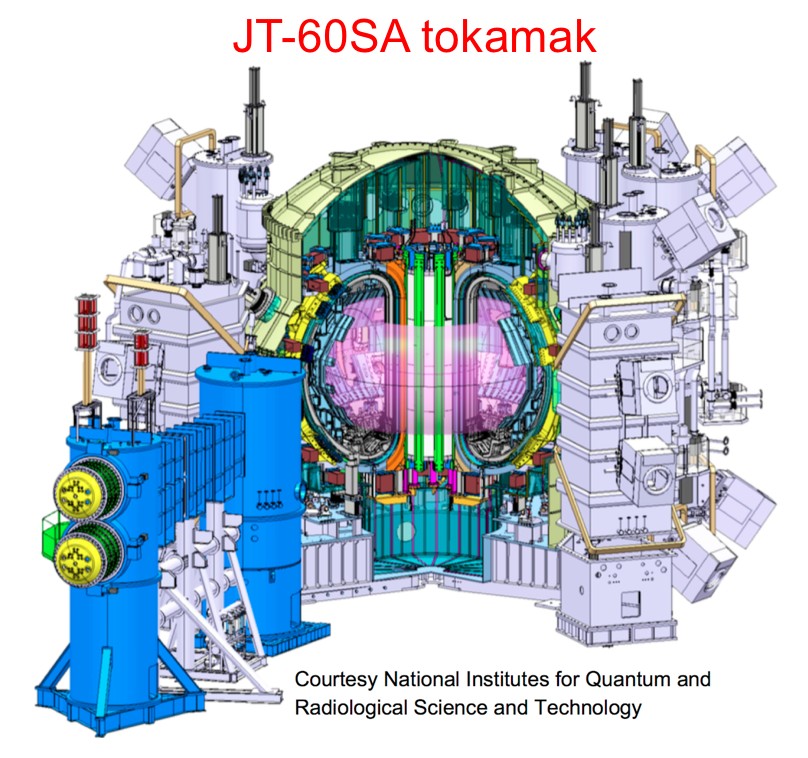
In 2020s, we will proceed to the next stage by operating new two new experimental machines: ITER and JT-60SA.
ITER is being built in France by an international collaboration (EU, Japan, US, Russia, China, South Korea, India) and will start its operation in 2025. ITER is the largest machine in the world. We will have controlled burning plasmas in ITER for the first time (in human history).
JT-60SA is the second largest machine. It is designed to explore more challenging operation scenarios than permitted on ITER. JT-60SA is about to start its operation in Japan through a collaboration between Japan and EU. We can say we are in a really exciting moment.
I and all other faculty members of the "Nuclear Fusion Research Education Program" would like to foster young scientists who can enjoy and lead these big projects.
For this purpose, my laboratory utilizes the spherical tokamak, TST-2, collaborating with the Ejiri-Tsujii Lab in Kashiwa campus and other facilities (JT-60SA, JT-60U, LHD, QUEST) under collaborations with QST*, NIFS* and other universities.
*)
QST: National Institutes for Quantum Science and Technology in Japan;
NIFS: National Institute for Fusion Science in Japan

Tel. 0572-58-2270
E-mail: todo@nifs.ac.jp
http://www.nifs.ac.jp/rd/fts/index-e.html
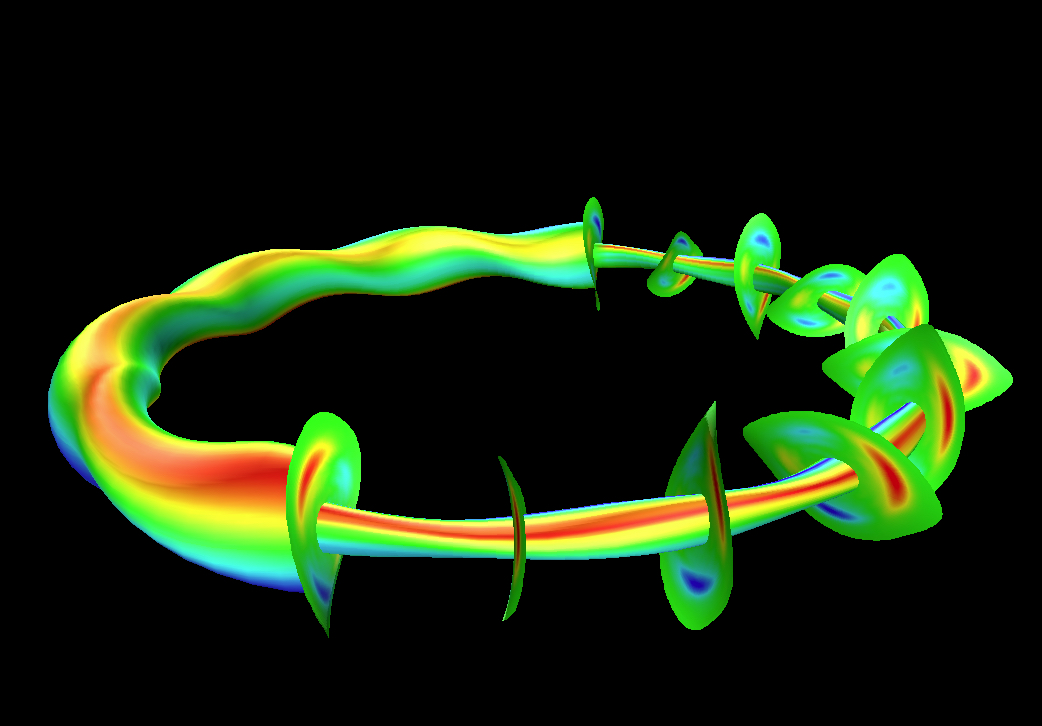
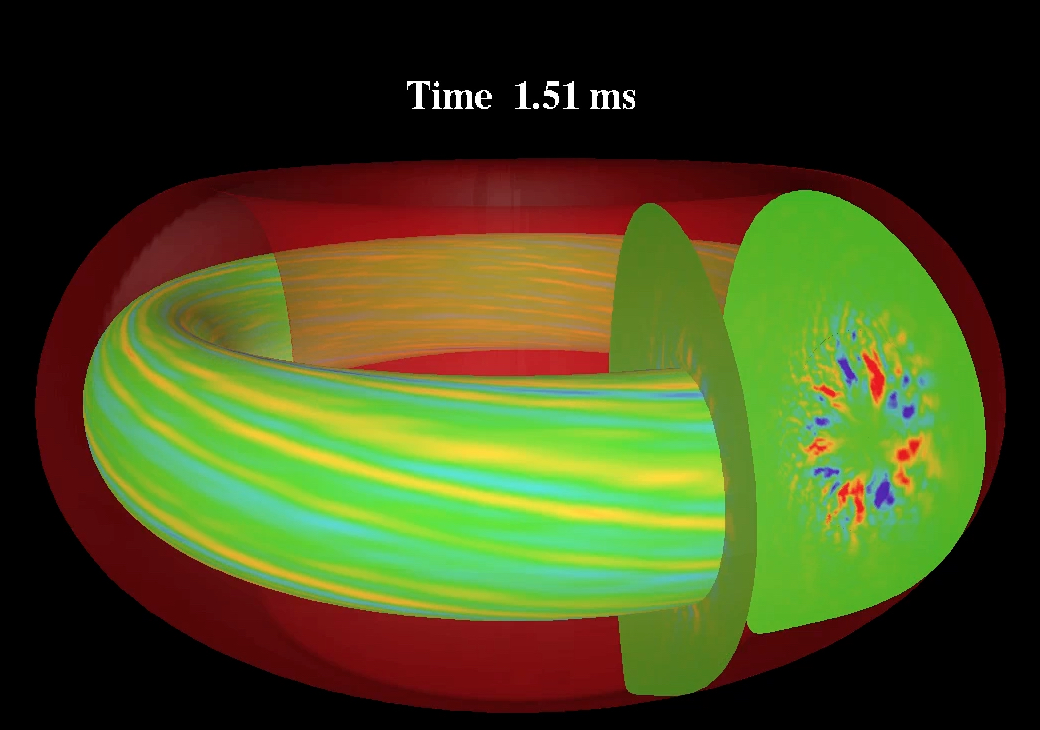
Plasma consists of a huge number of charged particle. The various behaviors of plasma brought about by the interaction between charged particles and the electromagnetic field are complex nonlinear problems. In order to clarify and predict the nonlinear phenomena of plasmas, we promote large-scale computer simulations using supercomputers.
Our primary research subject is the interaction between fast ions and magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) waves in magnetically confined fusion plasmas. This is an especially important subject for ITER, which is under construction in France with the international collaboration.
In addition, we conduct simulation studies of energetic particles and MHD phenomena, and develop computational physics models and high-performance computing methods. We also actively promote both domestic and international collaborations for many experiment devices such as the Large Helical Device (National Institute for Fusion Science) and the TST-2 Spherical Tokamak (University of Tokyo).
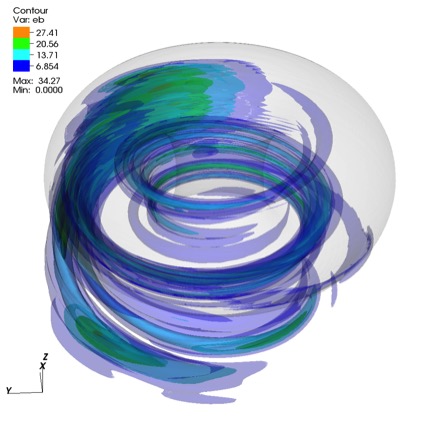
Figure caption: Fluid velocity fluctuation profiles of MHD waves in the Large Helical Device (left) and ITER (middle), and snapshot of laboratory (right).


Tel. 04-7136-3367
E-mail: okazaki@issp.u-tokyo.ac.jp
http://okazaki.issp.u-tokyo.ac.jp/
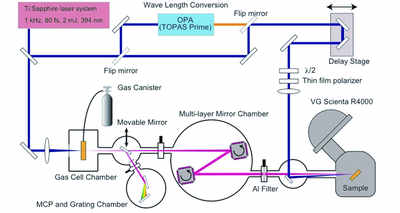
一緒に世界トップを目指して物質の世界を探求しよう』
Angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy is a very powerful experimental technique that can directly observe a dispersion relation between momentum and energy of the electrons in solid-state materials, whereas by utilizing a femtosecond laser as pumping light and its high harmonic generation as probing light, we can observe ultrafast transient properties of the band structures in a non-equilibrium state. In our group, we are developing and improving a time-resolved photoemission apparatus that utilize high harmonic generations of an ultrashort-pulse laser in collaboration with a laser-developing group. We are aiming for understanding the mechanisms of electron relaxations from photo-excited states and mechanisms of photo-induced phase transitions by direct observations of transient electronic states with a pump-probe type time-resolved photoemission spectroscopy. Also, we are aiming for understanding the mechanisms of unconventional superconductivity by direct observations of the electronic structures and superconducting-gap structures of unconventional superconductors with a laser-based angle-resolved photoemission apparatus with a world-record performance that achieves a maximum energy resolution of 70 micro eV and lowest cooling temperature of 1 K.